Executing a swap on Ethereum can pose a significant concern for traders due to the expensive gas expenses. Fortunately, this issue is mitigated to a certain extent by DEX aggregators that optimally determine the most profitable route, taking into account gas costs.
Source: Delphi Research
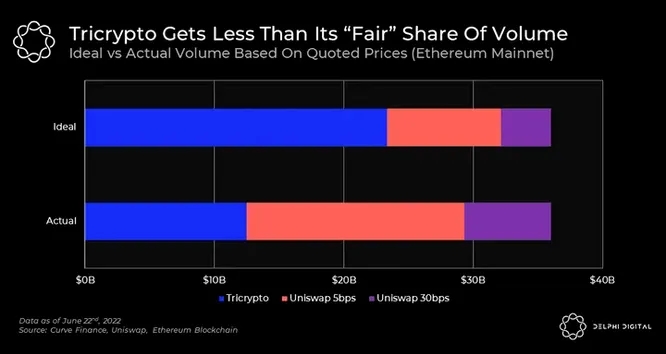
Our Uniswap vs. Curve report last year compared Uniswap and Curve’s performance. It was noted that despite offering superior prices ~65% of the time, Curve’s Tricrypto pool fell short of its ideal volume. It was reported that “the discrepancy between “ideal” and actual volume can be mainly attributed to gas costs. Since Curve v2 is more complex, the cost of a swap ranges from 250-300K gas versus 125-175K gas on Uniswap v3.”
Source: Delphi Research
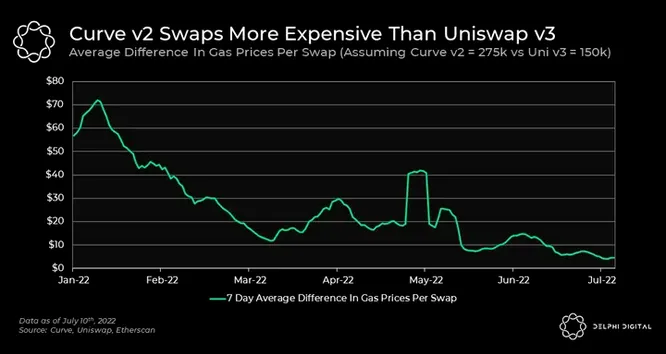
This disparity in gas costs proved substantial, reaching differences as high as ~$70 during periods of high demand.
Given that a lot of trades are channeled through DEX aggregators, the incorporation of gas costs is crucial for improved routing and furnishing traders with optimal quotes.
Let’s review some current advancements addressing gas optimization:
- Curve’s v2 Tricrypto contract is 3x more gas efficient than v1 by adjusting their calculation methodology.
- Uni v4 and Ambient Finance utilize a Singleton Contract, which allows for all pools and swaps to live under a single contract. Ambient has been extremely gas efficient when compared to Uni v3. It costs 30x less in new pool creations, 75% cheaper in adding a liquidity range, and swaps cost less than half.
There will likely be a significant shift in liquidity and changes in the DEX landscape once these protocols are fully deployed. Let the fight for gas optimization begin.